Food Systems
Food systems are complex, interconnected networks that encompass all aspects of food production, distribution, and consumption. They include the entire chain of activities from farm to fork, as well as the economic, social, and environmental factors that influence these processes.
Definition and Scope
Food systems comprise all elements and activities related to the production, processing, distribution, preparation, and consumption of food[1][2]. This includes:
- Production: Growing crops, raising livestock, fishing, and other forms of food production
- Aggregation: Collecting and storing food products
- Processing: Transforming raw ingredients into food products
- Distribution: Transporting and marketing food products
- Consumption: Purchasing, preparing, and eating food
- Disposal: Managing food waste and recycling
Food systems also encompass the broader economic, societal, and natural environments in which these diverse production systems are embedded[3].
Key Components
A comprehensive food system includes several interconnected components:
-
Core Value Chain: The primary activities directly involved in moving food from production to consumption[3:1].
-
Extended Value Chain: Supporting activities that provide inputs and services to the core value chain, such as:
- Seed and fertilizer production
- Agricultural research and development
- Extension services
- Financial services
- Equipment manufacturing
-
Enabling Environment: The broader context that influences food systems, including:
- Natural resources (land, water, biodiversity)
- Climate and environmental conditions
- Policies and regulations
- Cultural norms and consumer preferences
- Infrastructure and technology
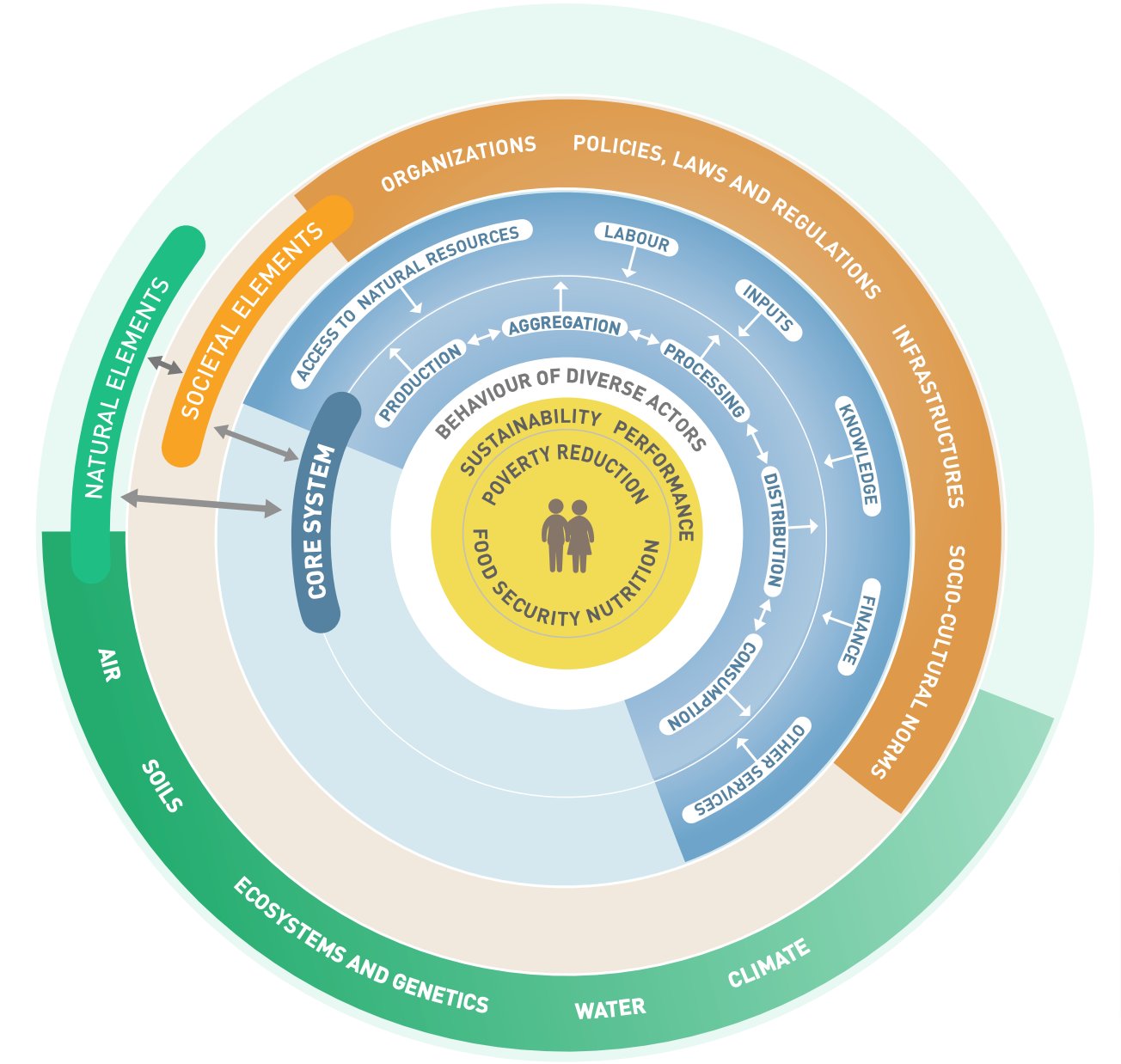
Figure 1. Food system wheel – elements and interactions (Source: FAO)
Sustainability and Challenges
A sustainable food system delivers food security and nutrition for all while ensuring economic, social, and environmental sustainability[1:1]. However, current food systems face several challenges:
- Rising hunger and malnutrition
- Impact of greenhouse gas emissions (about one-third of global emissions)[2:1]
- Biodiversity loss and environmental degradation
- Economic inequalities and rural poverty
- Food loss and waste (approximately one-third of food produced globally)[2:2]
Transformation Goals
International organizations are calling for a transformation of food systems to address these challenges. Key objectives include:
- Ensuring Food Security and improved nutrition for all
- Promoting economic sustainability and equitable livelihoods
- Reducing environmental impact and enhancing climate resilience
- Fostering innovation and sustainable practices throughout the value chain
https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/b620989c-407b-4caf-a152-f790f55fec71/content ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.worldbank.org/en/programs/food-systems-2030/food-systems-transformation ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
https://www.fao.org/climate-smart-agriculture-sourcebook/production-resources/module-b10-value-chains/chapter-b10-2/en/ ↩︎ ↩︎